数据加密传递
前言
在数字化飞速发展的今天,数据已经渗透到我们生活的方方面面。无论是个人信息的保护,还是企业核心资产的维护,数据安全都显得尤为重要。然而,随着网络攻击手段的不断升级,传统的安全防护措施已经难以满足日益增长的安全需求。因此,数据加密技术应运而生,成为保护数据传输安全的重要工具。本文以之前所写的 数据加密、自定义注解 博客为基础,来讲解在我们如今前后端分离模式下数据调用传输时如何进行统一加解密处理。
传输加密重要性
保护隐私和机密性
未经加密的数据在传输过程中容易被黑客、未经授权的第三方监听和截取。这可能导致敏感信息如个人身份、银行账号、商业秘密等泄露,给个人和组织带来严重的安全风险。如黑客可以通过
抓包等方式截取请求,从而拿到请求的数据。加密技术可以将明文数据转换为不可被直接读取的密文数据,只有拥有相应密钥的人才能解密还原出明文数据,从而确保数据的机密性。防止篡改
未加密的数据在传输过程中可以轻易被中间人修改或插入恶意内容,破坏数据的完整性和真实性。如中间人通过
抓包拿到请求后,可以修改请求内容进行二次转发模拟请求服务(例如羊了个羊游戏刚出时,很多排行榜中无限通关者都是通过此方式编写脚本刷关卡)。加密技术可以确保数据的真实性和完整性,任何对数据的非法更改在解密时都能被发现,从而防止数据被篡改。满足合规要求
许多行业和法规(例如《通用数据保护条例》GDPR)要求对特定类型的数据进行加密处理,以确保用户隐私和信息安全。
建立信任
对于在线交易和服务,如电子商务、网上银行、远程办公等场景,数据加密是构建用户信任的基础。使用加密技术可以确保用户与服务器间传输数据的安全,增强用户对服务的信任度。
防止拒绝服务攻击
加密本身不直接防止DoS/DDoS攻击,但它可以通过加密通信使得攻击者更难分析流量特征,从而增加攻击难度。有助于降低组织遭受拒绝服务攻击的风险和损失。
传输加密原理
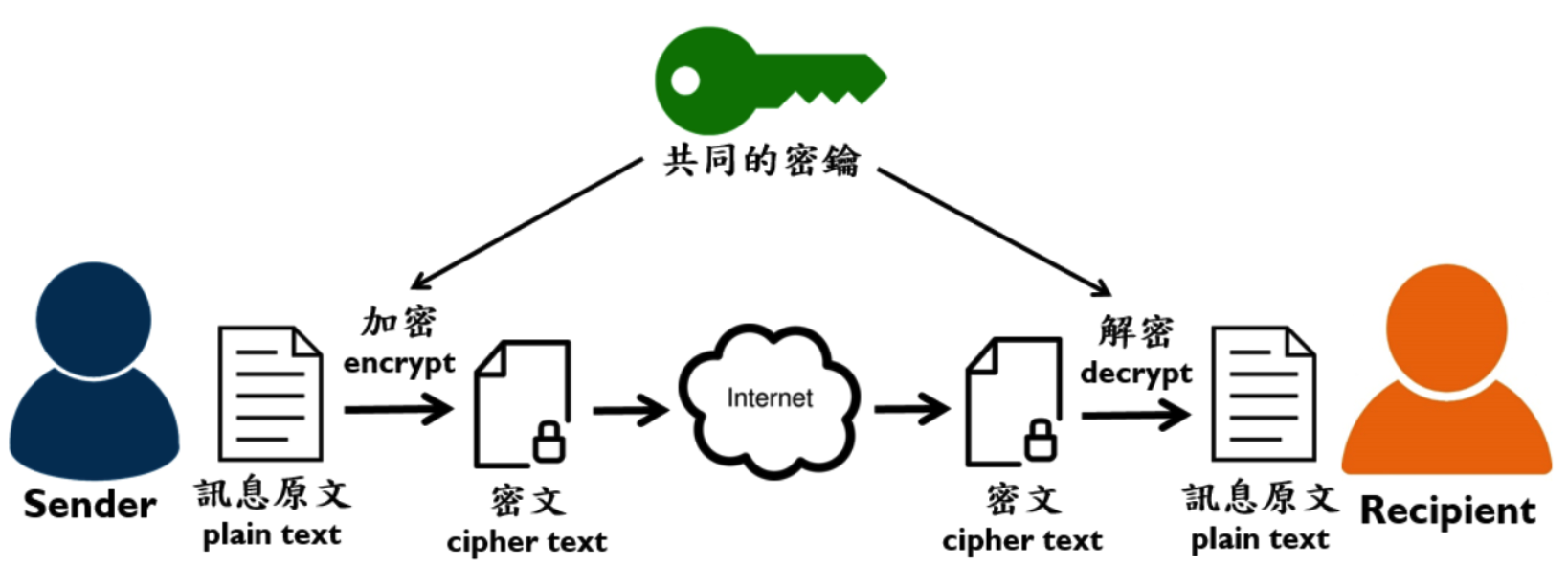
发送者和接收者使用同一密钥,发送者通过此密钥对原文数据加密后进行网络传输,接收者获取密文后通过密钥进行解密操作,从而得到原文数据。
发送者和接收者双方加密方式可自行约定,保证网络传输中所传递数据都为加密后密文数据即可
代码示例
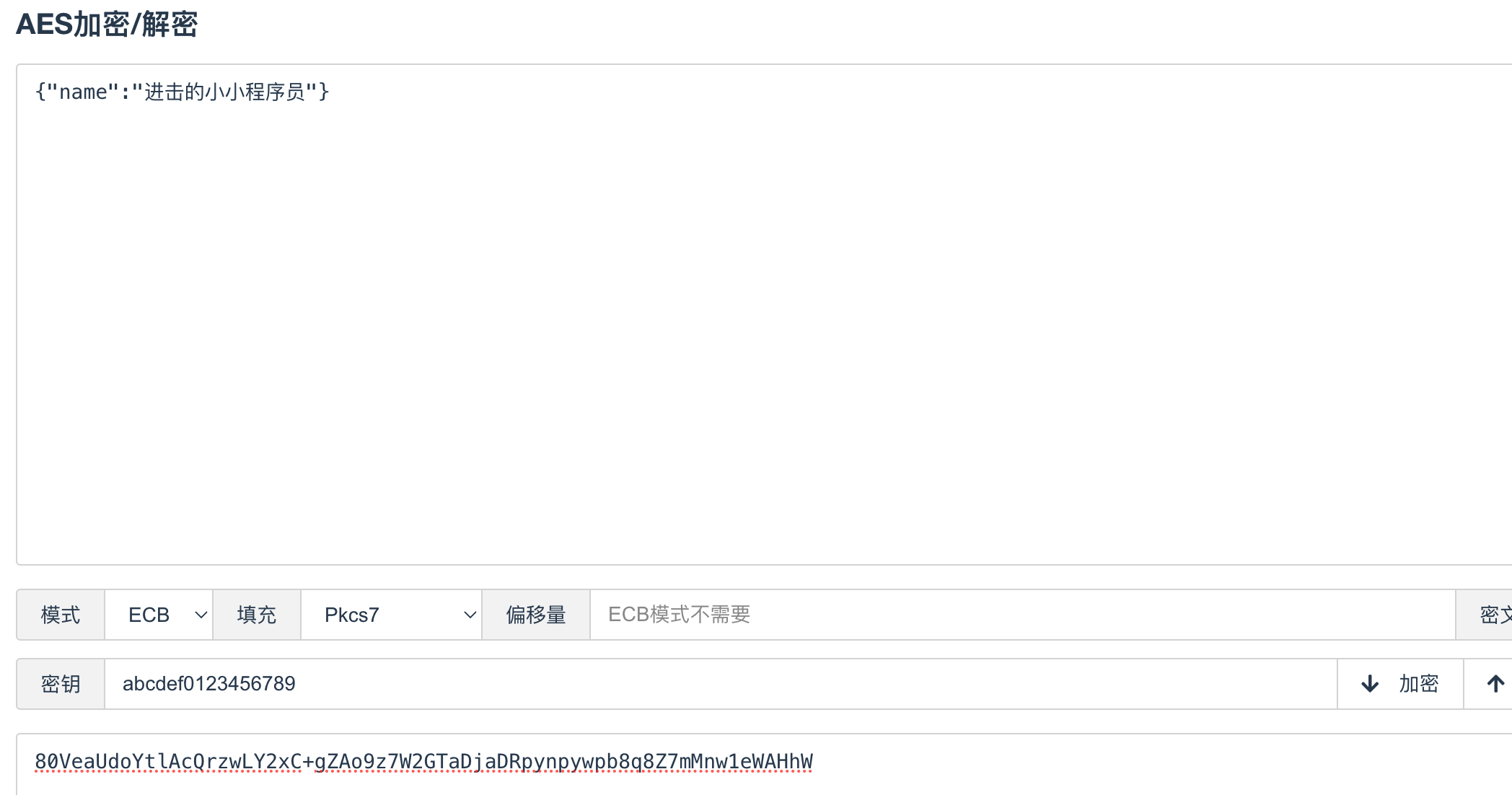
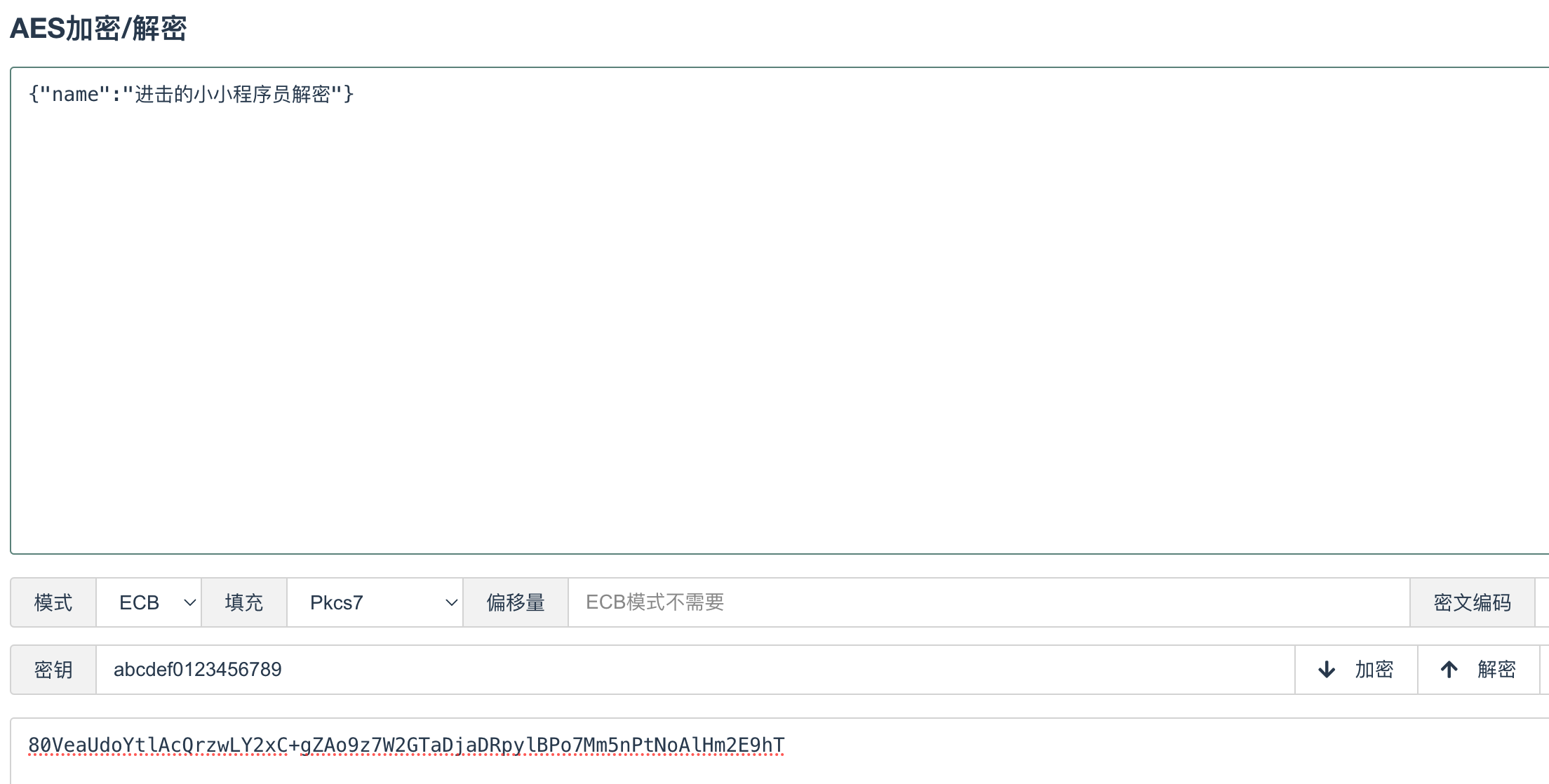
当前示例使用AES加密后进行数据传输,定义统一密钥为 abcdef0123456789 ,前后端都保存此密钥。
定义注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/***
* 自定义解密注解
* @author deng
* @date 2024/7/1
*/
public Decrypt {
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9/***
* 自定义加密注解
* @author deng
* @date 2024/7/1
*/
public Encrypt {
}定义加解密工具类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50/***
* 加解密工具类
* @author deng
* @date 2024/7/1
*/
public class AesUtils {
/***
* 定义加密方式和填充方式
*/
private static final String AES_ALGORITHM = "AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding";
/***
* 获取 cipher
* @param key
* @param model
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private static Cipher getCipher(byte[] key, int model) throws Exception {
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(AES_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(model, secretKeySpec);
return cipher;
}
/***
* AES加密
* @param data
* @param key
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static String encrypt(byte[] data, byte[] key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = getCipher(key, Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipher.doFinal(data));
}
/***
* AES解密
* @param data
* @param key
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static byte[] decrypt(byte[] data, byte[] key) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = getCipher(key, Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE);
return cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(data));
}
}定义数据加解密注解处理器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50/***
* 数据解密处理器
* @author deng
* @date 2024/7/1
*/
public class DecryptRequest extends RequestBodyAdviceAdapter {
/***
* 密钥
*/
private static final String KEY = "abcdef0123456789";
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return methodParameter.hasMethodAnnotation(Decrypt.class) || methodParameter.hasParameterAnnotation(Decrypt.class);
}
public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) throws IOException {
// 从请求流中获取参数
String jsonParam = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputMessage.getBody()))
.lines().collect(Collectors.joining(System.lineSeparator()));
JSONObject jsonObject = JSONUtil.parseObj(jsonParam);
// 约定请求数据都存于 data 中
String data = jsonObject.getStr("data");
byte[] body = data.getBytes();
try {
// 进行数据解密
byte[] decrypt = AesUtils.decrypt(body, KEY.getBytes());
// 将解密后数据重新过滤为请求流
final ByteArrayInputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(decrypt);
return new HttpInputMessage() {
public InputStream getBody() {
return inputStream;
}
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
return inputMessage.getHeaders();
}
};
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【请求数据解密失败】:{}", e.getMessage());
}
throw new ServiceException("请求数据解密失败");
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33/***
* 数据加密处理器
* @author deng
* @date 2024/7/1
*/
public class EncryptResponse implements ResponseBodyAdvice<R> {
private ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
/***
* 密钥
*/
private static final String KEY = "abcdef0123456789";
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(Encrypt.class);
}
public R beforeBodyWrite(R body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
try {
// 加密返回对象中 data 数据
if (body.getData() != null) {
body.setData(AesUtils.encrypt(om.writeValueAsBytes(body.getData()), KEY.getBytes()));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【响应数据加密失败】:{}", e.getMessage());
}
return body;
}
}定义控制器方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34/***
* 数据加密传输控制器
* @author deng
* @date 2024/7/1
*/
public class EncryptionController {
/***
* 测试数据解密
* @param param
* @return
*/
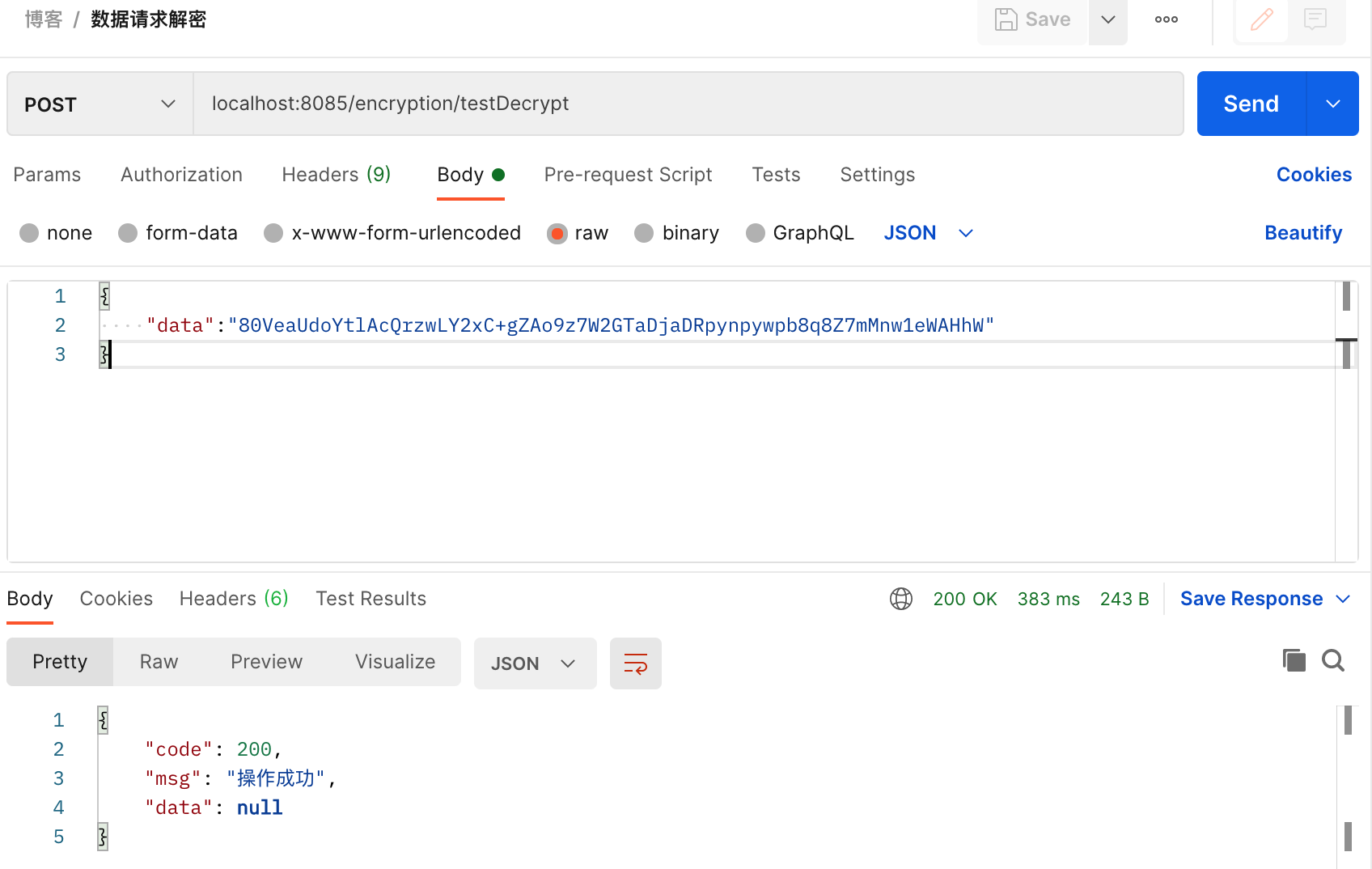
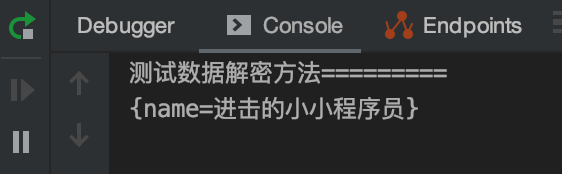
public R<Void> testDecrypt( Map<String, Object> param) {
System.out.println("测试数据解密方法=========");
System.out.println(param);
return R.ok();
}
/***
* 测试数据加密返回
* @return
*/
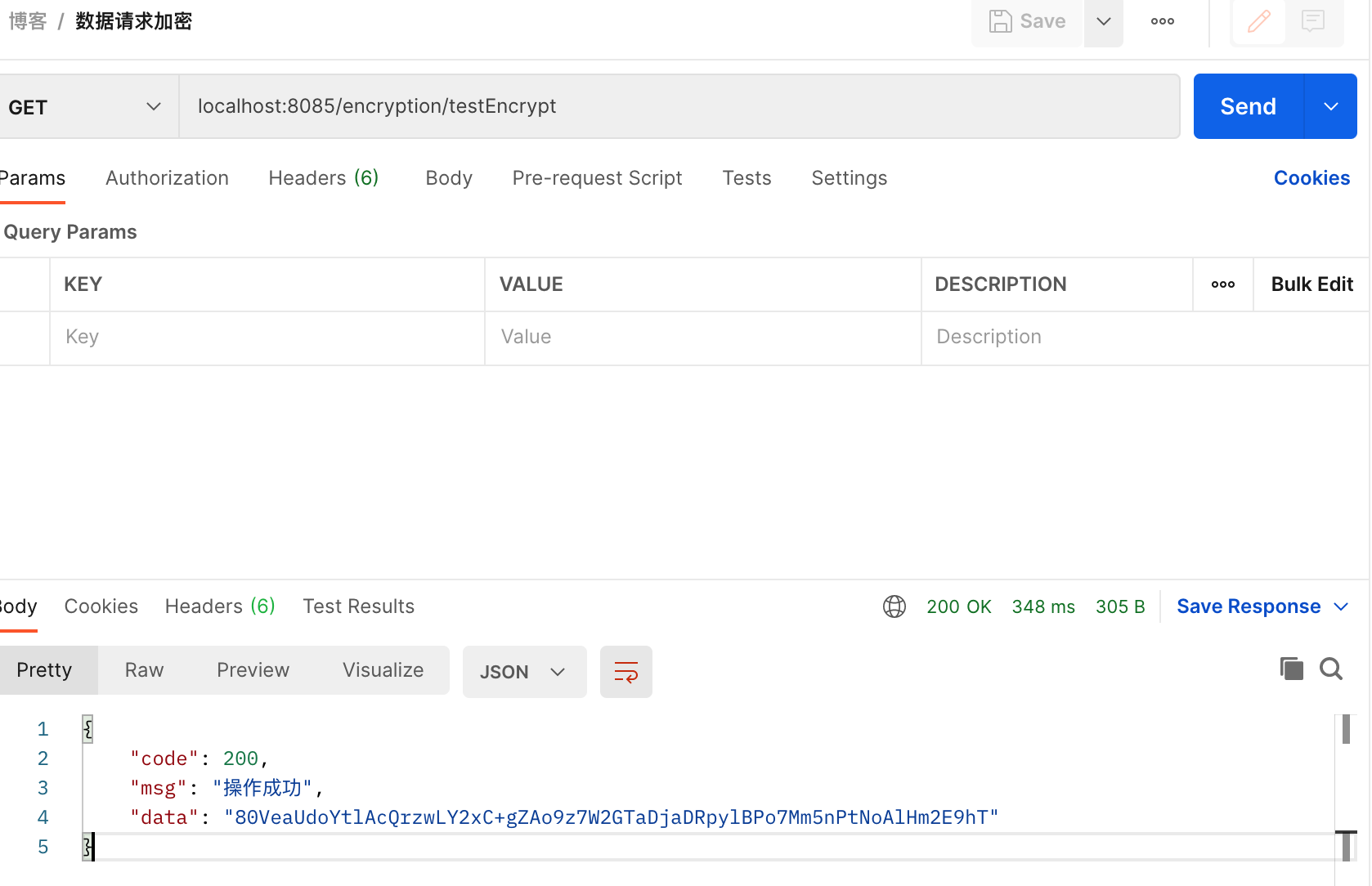
public R<Map<String, String>> testEncrypt() {
System.out.println("测试数据加密方法=========");
Map<String, String> map = MapUtil.builder("name", "进击的小小程序员解密").build();
return R.ok(map);
}
}Postman请求测试
前端加解密示例
通过JS加密库 Crypto-JS 进行数据传输加解密操作
安装加密库依赖
1
npm install crypto-js
创建 encrypt.js 工具库文件定义加解密方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45import CryptoJS from "crypto-js";
// 密钥
const SECRET_KEY = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse("abcdef0123456789");
// 十六位十六进制数作为密钥偏移量
const SECRET_IV = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse("abcdef0123456789");
/**
* 加密方法
* @param data
* @returns {string}
*/
export function encrypt(data) {
if (typeof data === "object") {
try {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign
data = JSON.stringify(data);
} catch (error) {
console.log("encrypt error:", error);
}
}
const dataHex = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse(data);
const encrypted = CryptoJS.AES.encrypt(dataHex, SECRET_KEY, {
iv: SECRET_IV,
mode: CryptoJS.mode.ECB,
padding: CryptoJS.pad.Pkcs7
});
return CryptoJS.enc.Base64.stringify(encrypted.ciphertext);
}
/**
* 解密方法
* @param data
* @returns {string}
*/
export function decrypt(data) {
const base64 = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.parse(data);
const str = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.stringify(base64);
const decrypt = CryptoJS.AES.decrypt(str, SECRET_KEY, {
iv: SECRET_IV,
mode: CryptoJS.mode.ECB,
padding: CryptoJS.pad.Pkcs7
});
return CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.stringify(decrypt).toString();
}加密传输
以用户登录API为例,在调用后端接口前进行加密处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15import {encrypt} from '@/utils/encrypt.js'
// 登录方法
export function login(username, password) {
const data = {
username,
password
}
let param = encrypt(data)
return request({
url: '/login',
method: 'post',
data: {data: param}
})
}